DataMapper와 MapStruct
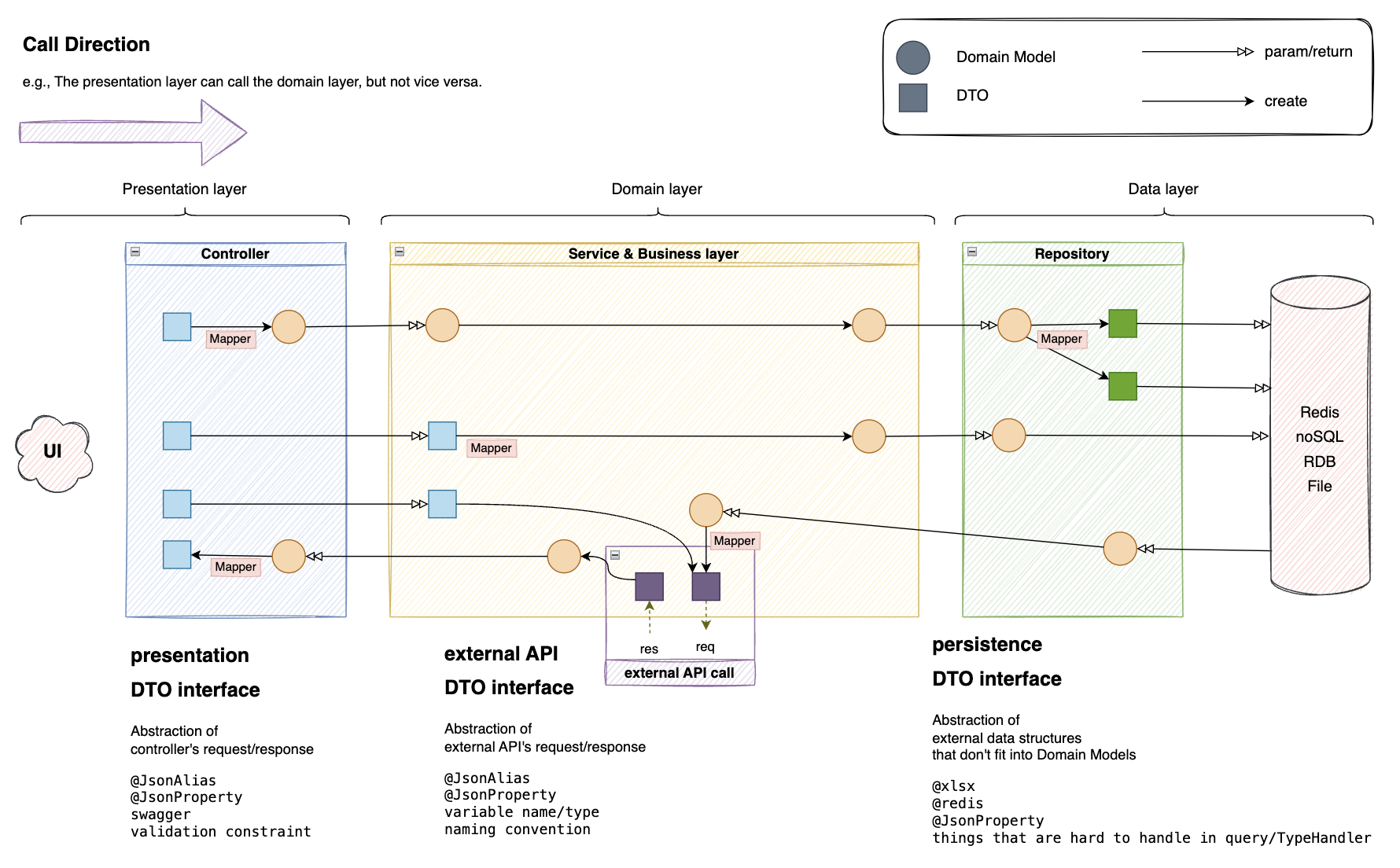
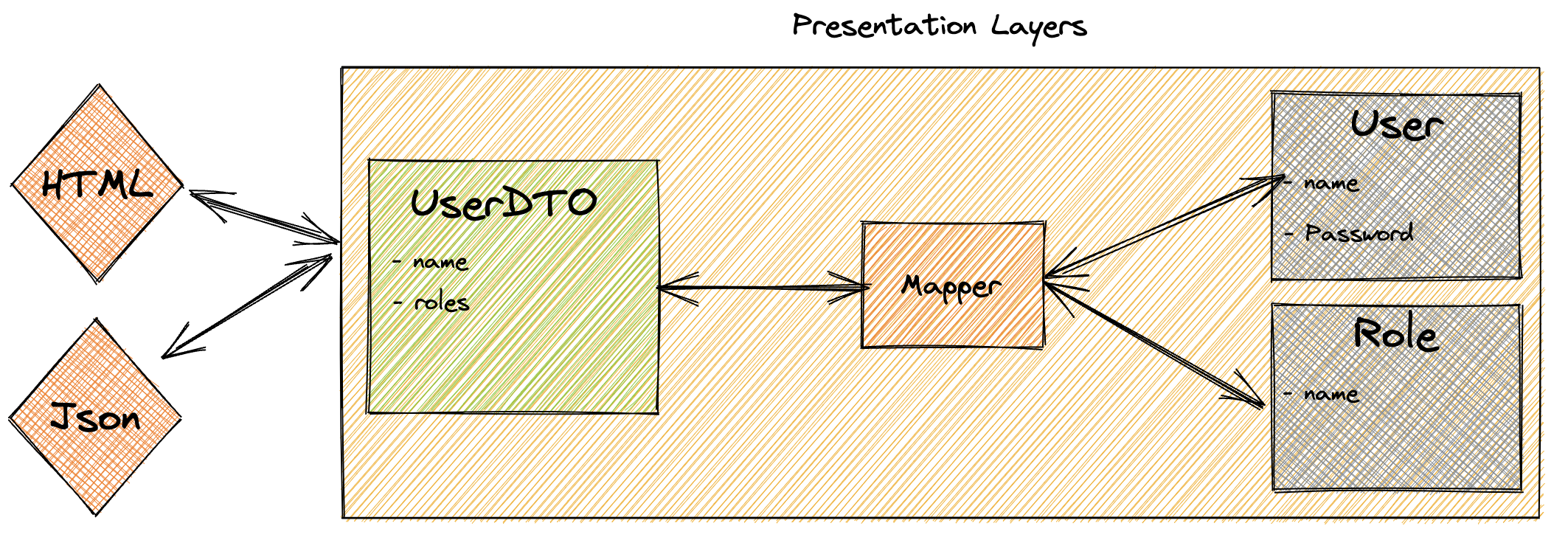 Presentation Layer 뿐만 아니라 어느 layer에서든 사용 할 수 있다. (e.g., Controller, Service, Repository 내에서)
Presentation Layer 뿐만 아니라 어느 layer에서든 사용 할 수 있다. (e.g., Controller, Service, Repository 내에서)
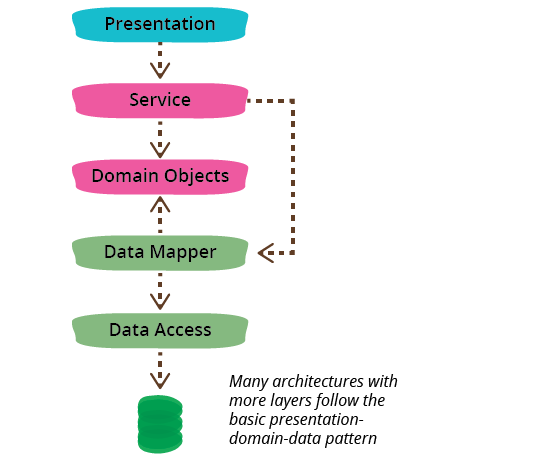
Data Mapper
[!tip] 요약 ) ‘Record<>Domain Model 매핑 로직’, ‘DTO<>Domain Model 매핑 로직’을 전담.
- Data를 다른 Data로 Mapping해주는 책임을 가진 구현체이면, 모두 Data Mapper다.
DTO<>Domain Model변환Record<>Domain Model변환- app 단의 data structure와 DataSource의 data structure가 1:1로 딱 들어맞지 않을 수 있기 때문에 이에 대한 변환이 필요하다.
- persistence layer 내에서 호출하는 경우, persistence layer의 역할 자체가 DataSource 추상화이므로, Data Mapper에도 DataSource specific한 코드가 들어갈 수 있다.
- Data Mapper를 하나의 layer로 보기 보다는, AOP 같은 느낌으로, 모든 layer에 걸쳐 Mapping이 필요한 부분에서 접근 가능한 개체로 보는 것이 더 유연해보인다.
MapStruct의 @Mapper
[!tip] 요약 ) 매핑 로직을 직접 작성 할 필요 없게, 자동으로 생성해주는 도구 (
build/generated에 생성되는 방식)
필요성
- layered architecture 지켜서 개발하다 보면, 기본적으로
presentation DTO -> Domain Model -> persistence DTO3단계 변환이 일어나고, 응답 반환에서도 똑같이 3단계 변환이 일어난다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
// presentation DTO
data class OutstandingRow(
val field1: String
) {
fun toModel(): Outstanding {
return Outstanding(
field1 = this.field1
)
}
companion object {
fun from(model: Outstanding) {
return OutstandingRow(
field1 = model.field1
)
}
}
}
// domain model
data class Outstanding(
val field1: String
)
// persistence DTO
data class OutstandingRecord(
val field1: String
) {
fun toModel(): Outstanding {
return Outstanding(
field1 = this.field1
)
}
companion object {
fun from(model: DomainModel) {
return OutstandingRecord(
field1 = model.field1
)
}
}
}
- 위와 같이
DTO<>Domain Model변환 메서드를 직접 작성하게 되면, 매핑 작업이 너무 많아 비효율적이다. (Data Mapper를 분리하지 않고DTO에 두었는데, Data Mapper를 분리해도 귀찮은 것은 똑같다.)- 간단한 작업인 경우, 매핑에 쓰는 시간이 전체 코드 작성 시간에서 너무 큰 포션을 차지해버린다.
- 도메인 모델에
field2가 추가되고, 이 것이 presentation/persistence DTO에도 추가되어야 하는 경우 매핑 함수도 다 고쳐주어야 한다. (간단한 코드임에도, 고쳐야 하는 포인트가 너무 많아 bad smell로 느껴진다)
- 이런 매핑 작업을 대신해주는 라이브러리가 MapStruct다.
예제
- https://mapstruct.org/의 Mapper interface 참조
1 2 3 4 5
@Mapper interface OutstandingMapper { fun toPresentation(model: Outstanding): OutstandingRow fun fromRecord(record: OutstandingRecord): Outstanding }
1 2
// usage private val outstandingMapper = Mappers.getMapper(OutstandingMapper::class.java)
참고
- https://martinfowler.com/eaaCatalog/dataMapper.html
- https://www.martinfowler.com/eaaCatalog/repository.html
- https://www.baeldung.com/java-dto-pattern
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/27996119/what-exactly-is-the-difference-between-a-data-mapper-and-a-repository
- 내가 생각하는 DDD 관점에서의 정의와 같다.
- https://proandroiddev.com/the-real-repository-pattern-in-android-efba8662b754
- DataSource 접근은 Repository에서, 변환(DTO <> Model)은 Mapper에서.
- 엔티티 클래스 설계와 퍼시스턴스 프레임워크 - benelog
- 좋은 글. DTO와 Domain Model에 대해서 까지.
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/jdbc/docs/current/reference/html/#jdbc.domain-driven-design
- DDD - aggregate와 repository에 대해서
- Domain Model에 대해서
- DataMapper는 MyBatis의 @Mapper와는 의미가 다르므로 주의
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.